linux iptables入门指南 代长亚 2024-10-31 2026-03-11 iptables 1、1 iptables防火墙简介 Netfileter/iptables (以下简称iptables)是nuix/linux 系统自带的优秀且完全免费的基于包过滤的防火墙工具、它的功能十分强大、使用非常灵活、可以对流入、流出及流经服务器的数据包进行精细的控制。特别是它可以在一台非常低配置下跑的非常好。提供400台机器的办公上网共享服务丝毫不逊色数万RMB企业级专业路由器防火墙
Iptables 是linux2.4及2.6内核中集成的服务、其功能与安全性比老一辈ipvfwadm、ipchanins强大的多、一般认为iptables工作在OSI七层的、二、三层、四层。
1、2 iptables 名词和术语 不少刚接触到iptables的初学者会被iptables防火墙的相关名词搞的很晕、不知道其所云的具体意思、本章不会像某些书籍一样长篇大论、而是以最基本的能让大家容易理解。
1、2、1 什么是容器 容器就是装东西的。如(箱、包、坛、)、容器就是用来包装或转载物品的存寄器、在iptables里的呢、就是用来描述这种包含或者说术语的关系、喜爱按我就来说说这些包含关系
1、2、2 什么是Netfileter/iptables Netfileter是表(tables)的容器,(还不知道啥意思的,请网上看)。这样解释大家肯定还晕、举例、如果吧Netfileter看成某小区的一栋大楼、那么表(tables)就是楼里的其中的一套房子。这套房子表(tables) 就属于这栋楼“Netfileter”。比如、你们家所在的小区所在楼当成netfileter
1、2、3 什么是表(tables) 表(tables)是链的容器、及所有的链(chains)都是属于表(tables),如上,如果把Netfileter看成某个小区的一栋楼、那么表(tables)就是楼里的某一套房子、比如你们家住的房子。当然了、表(tables)可能不止一个!
1、2、4 什么是链(chains)? 链(chains)是规则(Policys)的容器、链属于表,接上、如果表(tables)当做一套房子、那么链(chains)那么可以说是房子里的家具(桌子、柜子等)。每一套房子都可能会有桌子柜子等、
1、2、5 什么是规则(Policy) 规则(policy)就比较容易理解了、柜子(policy)属于链(chains)。就是iptables一系列过滤信息和具体操作方法、可以理解为购买什么家具、并且如何摆放、设计的更符合要求等、
1、2、6 整理个表格如下 描述完了基本术语我们画个形象的表格帮我们理解记忆下:
Netfileter/iptables
表(tables)
链(chains)
规则(policy)
小区的一栋楼
楼里的房子
房子里的柜子
增加、摆放的规则
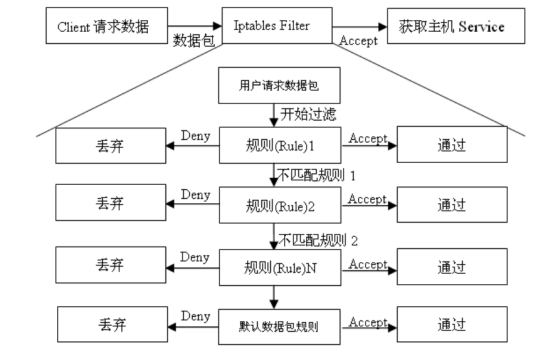
1、3 iptables工作流程 前面的介绍已经提到。Iptables 是采取数据包过滤机制工作的,所以它会对请求的数据包的包头数据进行分析、并根据我们预先设定的规则进行匹配来决定是否可以进入、流出、流经主机。下面我们以 iptables 进入主机进行过滤的流程图为例子
提示:
防火墙规则的执行顺序认为从前到后依次执行、遇到匹配的规则就不在继续向下检查、
如果遇到不匹配的规则则会继续向下进行。
重点: 匹配上了拒接规则也是匹配。因此不在继续向下进行、这一点大家要注意、
例如:同时执行了以下规则
[root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 3306 -j DROP
[root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 3306 -j ACCEPT
此时通过命令 telnet 192.168.132.194 3306 检查3306是不通的。原因就是telnet请求以匹配上了拒接规则、因此不会在找下面的允许规则、如果需要telnet 192.168.132.194 3306 连通、可以把ACCEPT规则中的-A 改为-I 即为 iptables –I INPUT –p tcp –dport 3306 –j ACCEPT 把允许规则防御INPUT链的第一行生效
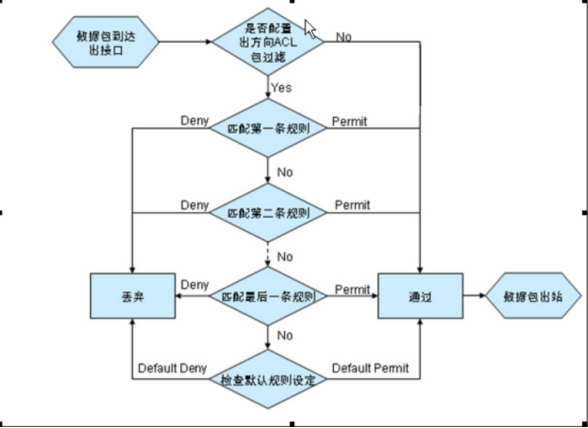
再来一个流程的图例:此里来自于交换机中acl过滤。如iptables 流程几乎一模一样。
入站数据包流程图:
出站数据包:
小提示:对于交换机的acl数据包过滤。除了顺序匹配外,还有深度匹配。即读完所有的再去匹配。匹配最精确的规则。
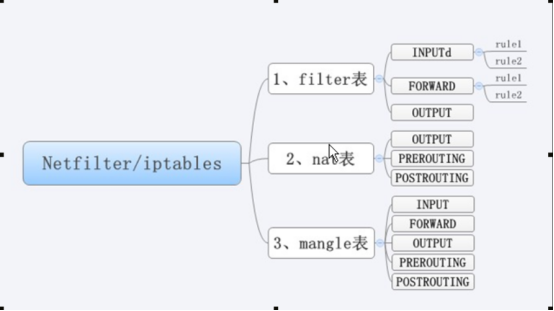
1、4 iptables 的表(tables) 和链(chains) 描述完iptables术语后、相信大家对iptables的表和链有了初步的了解了、默认情况下。Iptables,根据功能和表的定义划分、最常用的有三个表,分别是filter,nat mangle.其中每个表又有各自包含不同的操作链(chains)
小提示:如果你执行man iptables 可以发现还有raw表,不过我们不用理会它。平时我们几乎用不到。
西面的表格展示了表和链的对应关系。
特殊提示这里。我们画个思维辅导图辅助记忆
1、4、2 iptables 的filter表介绍
Filter表
和主机自身相关、负责防火墙(过滤本机流入、流出数据包)。
是iptables 默认使用的表、这个表定义了三个链( chains )说明如下
INPUT
负责过滤所有目标地址是主机(防火墙)地址的数据包、通俗的讲、就是过滤进入主机的数据包。
FORWARD
负责转发流经主机但不进入本机的数据包、起转发作用、和NAT 表关系很大、后面会详细介绍
OUTPUT
处理所有原地址是本机地址的数据包、通俗的讲就是处理从主机发出去的数据包。
对于filter表的控制是我们实现本机防火墙功能的重要手段。
1、4、3 iptabls 的nat表介绍 NAT表
是网络地址转换的意思。即负责来源与目的IP 地址和 port 的转换、和主机本身无关。一般用于局域网多人共享上网或者内网 IP 映射外网 IP 及不同端口转换服务等功能。 Nat表的功能很重要、这个表定义了三个链( chains )
OUTPUT
主机发出去的数据包有关、在数据包路由之前改变主机产生的数据包的目的地址等。
PREROUTING
在数据包刚到达防火墙时、进行路由判断之前执行的规则、改变包的目的地址(DNAT 功能)、端口等(通俗比喻,就是收信时、根据规则重写收件人的地址、这看上去不地道啊、)把公司 IP 映射到局域网的机器上、此链多用于把外部 IP 地址端口的服务、映射为内部 IP 地址及端口
POSTROUTING
在数据包离开防火墙时进行路由判断之后执行的规则、改变包的源地址(SNAT )、端口等(通俗比喻、就是寄信时写好发件人的地址、要让人家回信是能够有地址可回)刺链多用于局域网共享上网,把所有局域网的地址、转换为公网地址上
1、4、4 iptables 的mangle表介绍 Mangle
主要负责修改数据包中特殊的路由标记,如TTL 、 TOS 、 MARK 等、这个表定义了 5 个链( chains )
INPUT
同filter 表的 INPUT
FORWARD
同filter 表的 FORWARD
OUTPUT
同fileter 表的 OUTPUT
PREROUTING
同nat 表的 PREROUTING
POSTOUTING
同nat 表的 POSTOUTING
由于这个表与特殊路由标记有关、一般在生产运维工作中、我们很少用到这个mangle表。我们就不做详细介绍了、
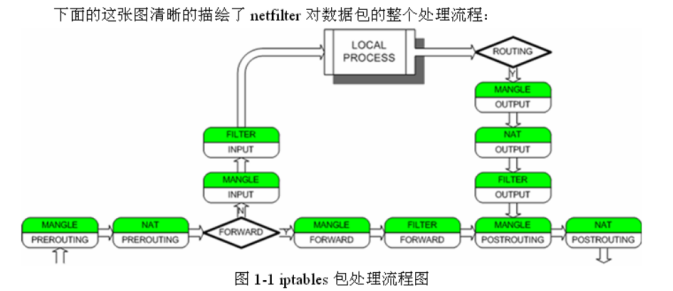
1、5 iptables 的表与链的工作流程
2、iptables 命令规则 2、1 iptables命令帮助信息。 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -h iptables v1.4.7 Usage: iptables -[AD] chain rule-specification [options] iptables -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification [options] iptables -R chain rulenum rule-specification [options] iptables -D chain rulenum [options] ###删除规则 iptables -[LS] [chain [rulenum]] [options] iptables -[FZ] [chain] [options] iptables -[NX] chain iptables -E old-chain-name new-chain-name iptables -P chain target [options] #(其中-p等同于 –policy规则) iptables -h (print this help information) Commands: Either long or short options are allowed. 提示:这款请注意。长格式短格式命令都可用、为了打字我们习惯于端格式 --append -A chain Append to chain --delete -D chain Delete matching rule from chain --delete -D chain rulenum Delete rule rulenum (1 = first) from chain --insert -I chain [rulenum] Insert in chain as rulenum (default 1=first) --replace -R chain rulenum Replace rule rulenum (1 = first) in chain --list -L [chain [rulenum]] List the rules in a chain or all chains --list-rules -S [chain [rulenum]] Print the rules in a chain or all chains --flush -F [chain] Delete all rules in chain or all chains --zero -Z [chain [rulenum]] Zero counters in chain or all chains --new -N chain Create a new user-defined chain --delete-chain -X [chain] Delete a user-defined chain --policy -P chain target Change policy on chain to target --rename-chain -E old-chain new-chain Change chain name, (moving any references) Options: [!] --proto -p proto protocol: by number or name, eg. `tcp' [!] --source -s address[/mask][...] source specification [!] --destination -d address[/mask][...] destination specification [!] --in-interface -i input name[+] network interface name ([+] for wildcard) --jump -j target target for rule (may load target extension) --goto -g chain jump to chain with no return --match -m match extended match (may load extension) --numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports [!] --out-interface -o output name[+] network interface name ([+] for wildcard) --table -t table table to manipulate (default: `filter') --verbose -v verbose mode --line-numbers print line numbers when listing --exact -x expand numbers (display exact values) [!] --fragment -f match second or further fragments only --modprobe=<command> try to insert modules using this command --set-counters PKTS BYTES set the counter during insert/append [!] --version -V print package version. [root@Nagios2 ~]#
2、2 实践iptables 命令规则 2、2、1 启动并查看iptables 1 2 3 [root@Nagios2 ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables start iptables: Applying firewall rules: [ OK ] [root@Nagios2 ~]#
查看iptables 的所有链和规则
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Iptables –L –n 或者 iptables –L –n –t filter 或者 iptables –L –n –x –v 中文说明: -L :列出一个或所有链的规则 -v:显示详细信息、包括每条规则匹配包数量和匹配字节数 -x:在v的基础上、进制自动单位换算(K,M) -n: 只显示IP地址和端口号码。不显示域名和服务名称 -t : 接表名、如果不加-t,默认就是 –t filter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -L -n Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT icmp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ACCEPT all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ACCEPT tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22 REJECT all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination REJECT all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
默认是filter的,没有加 –t 默认查看的就是如果想要查看NAT的表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -L -n -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination [root@Nagios2 ~]#
2、2、2 清除默认规则 为了从头学起,我们需要首先清除掉所有的默认规则、具体的命令为
1 2 3 Iptables –F ###清除所有规则 Iptables –X ####删除用户自定义的链 Iptables –Z ####链的计数器清零
提示:默认情况下,我们清除规则是对filter表的操作、如果是nat表、我们需要iptables –t nat –F
1 2 3 实例演示2: [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -F [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables –flush
2、2、3 iptables 规则语法 1)禁止ssh默认的22端口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP 提示: 1、iptables 默认用的就是filter表 。因此,以上两条命令等价。 2、其中INPUT DROP 等关键词要大写的 3、行为参数 --jump -j target 提示: target 的常见的处理方法有ACCEPT(接受),DROP(丢弃),REJECT(拒接)其中、一般不使用REJECT行为、REJECT会带来安全隐患、在这里我们只需要记住ACCEPT(接受)、DROP(丢弃)即可、
扩展:删除设定的规则
1 iptables –D INPUT –p tcp –dport 22 –j DROP
删除规则法二:
首先显示规则号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -L -n --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination 1 DROP tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:21 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination [root@Nagios2 ~]# [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -D INPUT 1
删除规则三:
执行iptables –F 清除所有的规则,临时生效。重启防火墙或重启计算机失效
删除规则法四:
重启防火墙/etc/init.d/iptables restart
禁止10.0.0.0/24 网段连入
1 2 iptables -A INPUT –i eth0 -s 10.0.0.0/24 -j DROP iptables -t filter -A INPUT –i eth0 -s 10.0.0.0/24 -j DROP
iptables 默认的标记是filter表。因此上两条命令等价。
测试 【! 非】
1、源地址不是192.168.132.201 的禁止连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 iptables –A INPUT –I eth1 –s ! 192.168.132.201 –j DROP iptables –A INPUT –I eth1 –s ! 192.168.132.201 –j ACCEPT [root@Nagios2 ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -i eth0 -s ! 192.168.132.1 -j DROP 小提示: 1) 这里-i eht0表示数据包的进入接口为eth0、类似的参数还有-o匹配数据流出的网络接口 例如:-o eth1 表示数据包的进入接口为eth1. 记忆方法: -in-interface –i [!] input name [+] Network interface name ([+] for wildcard) -out-interface –o [!] ouput name[+] Network interface name ([+] for wildcard)
2、源地址不是192.168.132.0/24 的禁止连接
1 2 3 iptables -A INPUT -s ! 192.168.132.0/24 -j DROP 等价于 Iptables –t filter –I INPUT –i eht0 –s ! 192.168.132.0/24 –j DROP
3、封掉3306端口
1 iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –dport 3306 –j DROP
4、匹配指定协议
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Iptables –A INPUT –p tcp Iptables –A INPUT –p udp 小提示:-p 参数可以匹配协议名或者协议号。 --proto –p [!] porto The specified protocol can be one of tcp,udp ,icmp.or all
5、匹配协议外的所有协议
1 Iptables –A INPUT –p ! tcp
6、匹配主机
1 2 3 Iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.132.10 Iptables –A INPUT –s ! 192.168.132.10
7、匹配网段
8、匹配端口之外的端口
1 Iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –dport !22 -j DROP
9、匹配端口范围
1 2 3 4 5 Iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –sport 22:80 ###源端口的22 和80端口就是来访主机的端口 iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dport 21,22,23,24 -j ACCEPT ###目的端口。就是本地端口 Iptables –I INPUT –p tcp –dport 3306:8809 –j ACCEPT
10、匹配ICMP端口和ICMP类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Iptables –A INPUT –p icmp –icmp-type 8 例如:iptables –A INPUT –p imcp –icmp-type 8 –j DROP Iptables –A INPUT –p icmp –m icmp –icmp-type any –j ACCEPT Iptables –A FORWARD –s 192.168.132.0/24 –p icmp –m icmp –icmp-type any –j ACCEPT
11、匹配指定的网络接口
1 2 3 Iptables –A INPUT –i eth0 ###进入端口的数据包 Iptables –A INPUT –o eth1 ###出入的端口数据包
12、安全保护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Syn-flood protection; [root@Nagios4 ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --syn -m limit --limit 1/s -j ACCEPT Furtive port scanner : [root@Nagios4 ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST RST -m limit --limit 1/s -j ACCEPT Ping of death: [root@Nagios4 ~]# iptables -A FORWARD -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -m limit --limit 1/s -j ACCEPT
2、2、4 生产环境常用服务的iptables 规则实践
特别提示:以下规则是以默认规则为拒接规则设计
仅允许内部合法的IP访问服务器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #setting access rules #one ,ip access rules,allow all the ips of iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.132.0/24 -p all -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -s 120.42.60.51/27 -p all -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p all -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.20.0/24 -p all -j ACCEPT
仅允许内部合法的ip段ip访问监控服务nagios
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #second.port access rules #nagios iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.132.0/24 –p tcp –dport 5666 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 200.100.59.0/24 –p tcp –dport 5666 –j ACCEPT
仅允许内部合法ip段访问mysql数据库和oracle数据库
1 2 3 4 5 #db iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.10.0/24 –p tcp –dport 3306 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.50.0/24 –p tcp –dport 1521 –j ACCEPT
仅允许内部合法IP段访问SSH远程连接服务
1 2 3 #ssh difference form other servers here…… iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –s 192.168.10.0/24 –dport 50718 –j ACCEPT
对HTTP服务的不同限制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a、对外提供HTTP服务的业务,要允许http服务通过、并且不限制IP #http iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –dport 80 –j ACCEPT b、对内部提供http服务的业务、一般用特殊端口、并且限制合法IP连接或者VPN连接 iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.132.0 –p tcp –m multiport –dport 8080,8081,8082,8888 –j ACCEPT
6、snmp的限制
1 2 3 4 5 iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.132.0/24 –p UDP –dport 161 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.155.0/24 –p UDP –dport 161 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.166.0/24 –p UDP –dport 161 –j ACCEPT
7、 rsync 服务的限制策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # rsync iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.132.0/24 –p tcp –m tcp –dport 873 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.12.0/24 –p tcp –m tcp –dport 873 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.1.0/24 –p tcp –m tcp –dport 873 –j ACCEPT
8、 nfs 服务的限制
1 2 3 iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.10.0/24 –t TCP –m multiport –dport 111,892,2049 –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –s 192.168.100.0/24 –t TCP –m multiport –dport 111,892,2049 –j ACCEPT
9、ftp服务的限制
1 2 3 4 5 iptables –A INPUT –p tcp –dport 21 –j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
提示:上面内容表示对已经建立连接的数据包、或者发出去的数据包允许通过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 说明 iptables –A INPUT –m state –state 状态 –j ACCEPT 下面几种 1) INVLID #####不可用的。数据包不能被识别。比如说内存溢出。ICMP错误 2) ESTABLISHED ###这个包已经建立了连接、 3) NEW ####这个包已经开始新连接了。然后也是有双向的。但是还看不见 4) RELATED ####这个包开始了一个新连接。并且和已经存在的连接已经有关联。
icmp 协议的限制
1 2 3 4 5 iptables –A INPUT –p icmp –icmp-type any –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –p icmp –s 192.168.10.0/24 –m icmp –icmp-type any –j ACCEPT iptables –A INPUT –p icmp –icmp-type 8 –j ACCEPT
提示:如果不想开。就不执行此行